The Design – Ethylene Glycol + Water Liquid Through Car Radiator Cooling System | Ansys CFX
This simulation is about an Analysis of Ethylene Glycol + Water Liquid Through Car Radiator Cooling System using ANSYS CFX software. We perform this CFD project and investigate it by CFD analysis.
A car’s radiator cooling system circulates coolant to absorb heat from the engine and dissipate it into the air. This process involves a water pump to circulate the coolant, a thermostat to regulate its flow, and a radiator with fins and a fan to cool the liquid before it returns to the engine. The entire system works continuously to keep the engine at an optimal operating temperature.
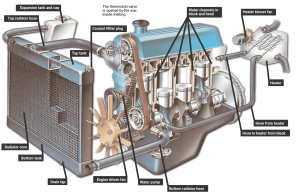
Picture 1. A car’s radiator cooling system
Components and function
- Coolant: A mixture of water and antifreeze that absorbs heat from the engine.
- Water Pump: Circulates the coolant through the engine and the radiator. It’s typically driven by a belt.
- Thermostat: Controls the coolant’s flow. It remains closed when the engine is cold to help it warm up, and opens to allow coolant to flow to the radiator once the engine reaches its proper operating temperature.
- Radiator: The main heat exchanger. Hot coolant enters the radiator, flows through its fins, and transfers heat to the air passing through.
- Radiator Fan: Sits behind the radiator to pull air through the fins, especially at low speeds or when stopped. Some systems use a fan clutch that engages based on temperature, while others use electric fans.
- Hoses: Carry the coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components like the heater core.
How the system works
- Heat absorption: The water pump sends coolant through channels in the engine block, where it absorbs heat.
- Thermostat regulation: The hot coolant is pushed to the radiator. If the engine is cold, the thermostat stays closed, and the coolant circulates within the engine block to warm it up faster.
- Heat dissipation: Once the engine is warm, the thermostat opens. The hot coolant flows into the radiator’s upper tank, then through small tubes with fins. Air flowing through these fins (either from the car’s movement or the fan) removes heat from the coolant.
- Recirculation: The now-cooled coolant exits the radiator and returns to the engine via the water pump to repeat the cycle.
In this analysis, it has been made to simulate and analyze Ethylene Glycol + Water Liquid Through Car Radiator Cooling System using ANSYS CFX software.
Geometry & Grid
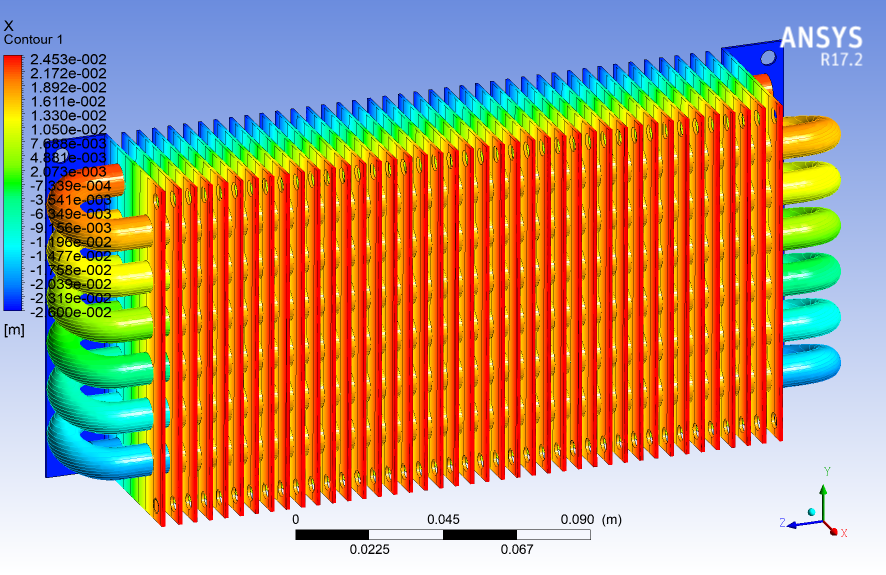
The geometry required for this analysis was generated by the Ansys Design Modeler software. The meshing required for this analysis was also generated by Ansys Meshing software. The mesh type used in this analysis is unstructured. The total number of volume properties for geometry is 4,9112e+005 mm³.
Model
In this analysis, a transient analysis type was used to obtain the results to check the fluid flow. In this analysis, non-buoyant models have been used, and stationary domain motion has also been activated in this analysis.
Boundary Condition
The flow input for this geometry of a Car Radiator directs the flow of air at a fluid temperature of 25°C into the geometry. The coolant material is considered Ethylene Glycol + Water Liquid through a Car Radiator. The turbulence boundary condition of a Car Radiator wall is considered to be none (laminar) according to the working conditions. The wall function is defined as automatic in the name selection section of the turbulence boundary condition. The mass flow rate for the mass momentum is equal to 0.004 kg/s. The Ethylene Glycol mass fraction for the component details is set with equal to 1.
Discretization of Equations
In this analysis, high resolution is used for the advection scheme of the basic settings. In this analysis, the first-order is used for turbulence numerics. In this analysis, the residual type of convergence criteria is RMS, and the residual target of convergence criteria is 0,0001.
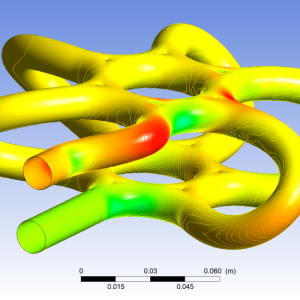
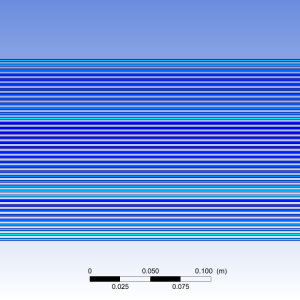
The results are presented as X contour 1 and Y contour 2.
The Design Services
We also accept all CFD projects using ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX. Our workshop has gathered experts in different engineering fields so as to ensure the quality of CFD simulations. One of our objectives is to boost the use of powerful computational fluid dynamics methods and also teach the engineers and those who seek professional knowledge in CFD.
ِDoing CFD projects will be faster and easier with our services. Call us for training in CFD applications and CFD packages. Our professional CFD engineers offer you professional consultation and technical supports for your academic CFD projects and industrial CFD projects. We offer you CFD learning, CFD project by ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX, CFD consulting by ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX, CFD service by ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX project, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX thesis, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX simulation, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX paper regeneration, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX academic project, ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS CFX industrial project, ANSYS Fluent, and ANSYS CFX research project, and low CFD Price. Moreover, we have years of experience in coordinating CFD projects. Therefore, we are ready to perform your CFD simulations in different engineering fields.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.